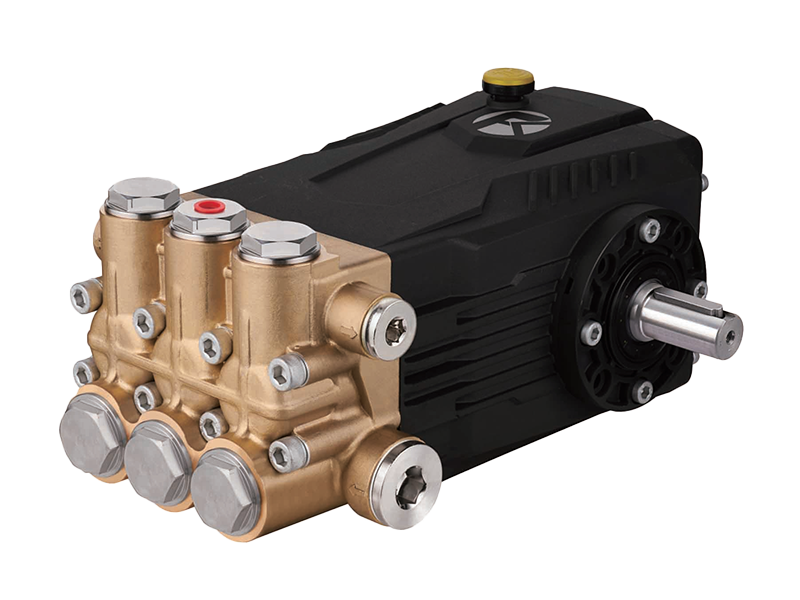
Compatibility of High Pressure Pumps with Various Voltage Levels and Power Frequencies
Introduction to Electrical Compatibility in High Pressure Pumps
High Pressure Pumps are essential components in many industrial systems, often requiring reliable power sources to function. One important consideration when selecting or operating these pumps is their compatibility with different voltage levels and power frequencies found in industrial electrical grids worldwide. Ensuring that a high-pressure pump can adapt to varying electrical standards is critical for performance, safety, and longevity.

Variations in Industrial Power Supply Standards
Industrial power grids differ significantly across regions, primarily in voltage levels and frequencies. Common voltage standards range from low voltages like 110V or 220V to higher levels such as 380V, 400V, or even 480V for three-phase systems. Meanwhile, power frequencies typically are either 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the country. This variability means that a high-pressure pump designed for one electrical standard might not operate correctly or safely if connected to an incompatible supply.
Impact of Voltage Differences on Pump Operation
When a high-pressure pump operates at a voltage lower or higher than its rated value, it can experience performance issues. Undervoltage can cause the pump’s motor to draw excessive current to maintain torque, resulting in overheating and potential damage. Overvoltage, on the other hand, may cause excessive speeds or increased mechanical stress. Proper matching of the pump’s motor voltage rating with the supply voltage is essential to maintain efficiency and avoid premature failure.
Frequency Compatibility and Motor Speed Considerations
The frequency of the electrical supply directly affects the speed at which the pump motor operates. For instance, a motor designed for 60 Hz will run slower on a 50 Hz supply, reducing the flow rate and pressure output. Conversely, running a 50 Hz motor on a 60 Hz supply increases speed and load, potentially causing mechanical wear or vibration issues. Therefore, the frequency must be considered alongside voltage to ensure the High Pressure Pump delivers the expected performance.
Design Features Enabling Multi-Voltage and Frequency Compatibility
Some high-pressure pumps are designed with flexible electrical systems to accommodate a range of voltages and frequencies. Motors with dual or triple voltage ratings and winding configurations that can be switched enable use across different power grids. Additionally, pumps paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs) offer even greater adaptability by controlling motor speed and allowing operation at various frequencies while protecting against electrical faults.
Installation and Conversion Challenges
Installing a High Pressure Pump in a location with a differing voltage or frequency may require transformers or converters to match supply specifications. While these solutions enable compatibility, they add complexity, cost, and potential points of failure. Proper engineering assessment and professional installation are necessary to ensure electrical compatibility without compromising pump performance or safety.
Conclusion: Ensuring Reliable Pump Operation Across Electrical Environments
In summary, the compatibility of a High Pressure Pump with different industrial voltage levels and power frequencies is a crucial factor for efficient and safe operation. Pumps designed with multi-voltage motors or equipped with variable frequency drives offer flexibility for global use. However, careful consideration of electrical standards, proper equipment matching, and professional installation remain essential to maintain the pump’s reliability and lifespan across various industrial power systems.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский










