Examining Efficiency Loss and Overheating Risks in Continuous Operation of High-Pressure Pumps
Overview of Continuous Operation Challenges in High Pressure Pumps
High Pressure Pumps are critical components in many industrial processes, often required to operate continuously for extended periods. While designed for durability and high performance, prolonged operation can sometimes cause challenges such as efficiency decline and overheating. Understanding these issues is essential for ensuring reliable pump performance, reducing downtime, and extending equipment lifespan.
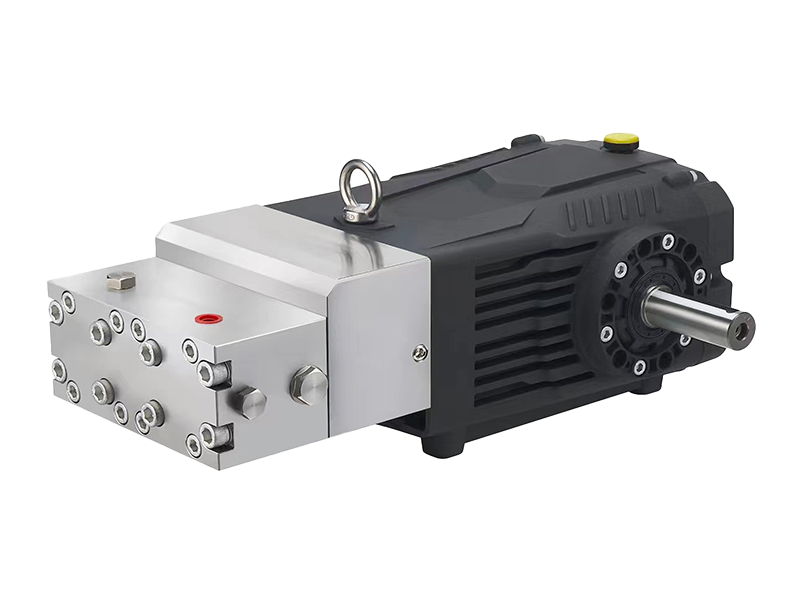

Factors C:ausing Efficiency Decline During Continuous Operation
Efficiency in a high-pressure pump refers to its ability to convert input energy into fluid movement effectively. Over time, continuous running can cause wear and tear on internal components like seals, bearings, and impellers, which in turn increases friction and reduces mechanical efficiency. Additionally, accumulated deposits or corrosion inside the pump may restrict fluid flow, causing increased resistance and lowered hydraulic efficiency. Operating conditions such as fluctuating pressure or improper alignment can exacerbate these effects.
Overheating Risks and Their Causes
Overheating is a significant concern during continuous pump operation. Excessive heat generation primarily results from friction in moving parts and energy losses in the motor driving the pump. Insufficient cooling, poor lubrication, or blockage in fluid flow can raise the pump’s internal temperature beyond safe limits. Electrical issues such as voltage imbalance or overload also contribute to motor overheating. Without adequate temperature control, sustained overheating may damage components and cause premature failure.
Design Features That Mitigate Efficiency Loss and Overheating
Modern High Pressure Pumps incorporate various design elements to address these challenges. High-quality materials with low friction coefficients and advanced seal technologies reduce mechanical wear. Some pumps feature built-in cooling systems, such as water jackets or heat exchangers, to dissipate heat effectively during operation. Variable speed drives help optimize motor load and prevent unnecessary strain, thereby maintaining efficiency and controlling temperature.
Maintenance Practices to Preserve Performance in Continuous Use
Proper maintenance plays a vital role in preventing efficiency decline and overheating. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn parts, routine lubrication, and cleaning of internal passages ensure smooth operation. Monitoring systems equipped with temperature and vibration sensors enable early detection of abnormal conditions, allowing operators to take corrective actions before serious damage occurs. Scheduled maintenance intervals based on operational hours or performance metrics help maintain suitable pump health.
Impact of Operating Conditions on Long-Term Reliability
Operating parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and fluid properties significantly influence the pump’s ability to sustain efficient, cool operation. Running the pump at or near its design limits continuously can accelerate wear and increase the risk of overheating. Conversely, operating well within recommended specifications generally extends equipment life. Careful process control and pump selection tailored to specific application needs are essential for balancing performance and longevity.
Conclusion: Ensuring Efficient and Safe Continuous Pump Operation
In summary, while High Pressure Pumps are engineered to handle continuous operation, efficiency loss and overheating remain potential issues if not managed properly. Design advancements, appropriate maintenance, and adherence to operating guidelines are key to mitigating these risks. By focusing on these aspects, industries can ensure reliable pump performance, reduce downtime, and achieve cost-effective, long-term operation in demanding environments.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский










