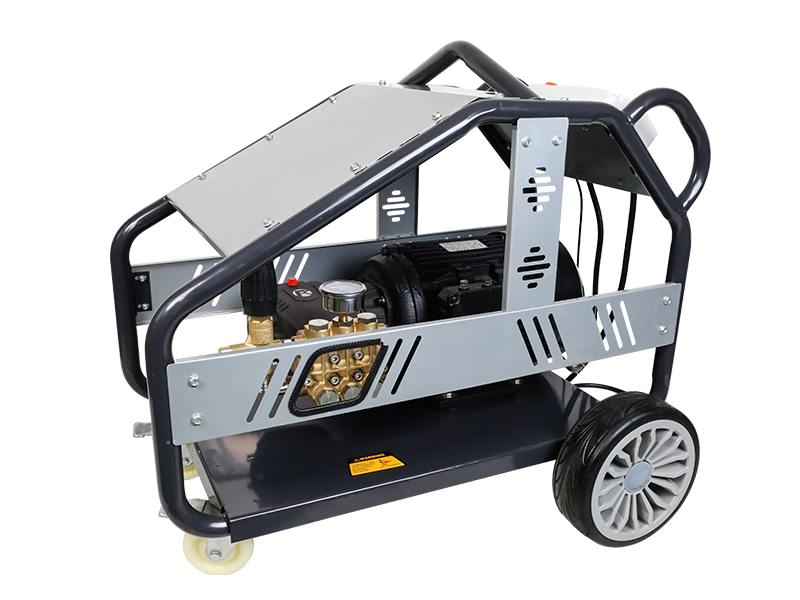
Assessing the Corrosion Resistance of High Pressure Pumps for Industrial and Harsh Environment Applications
Introduction to Corrosion Challenges in High Pressure Pumps
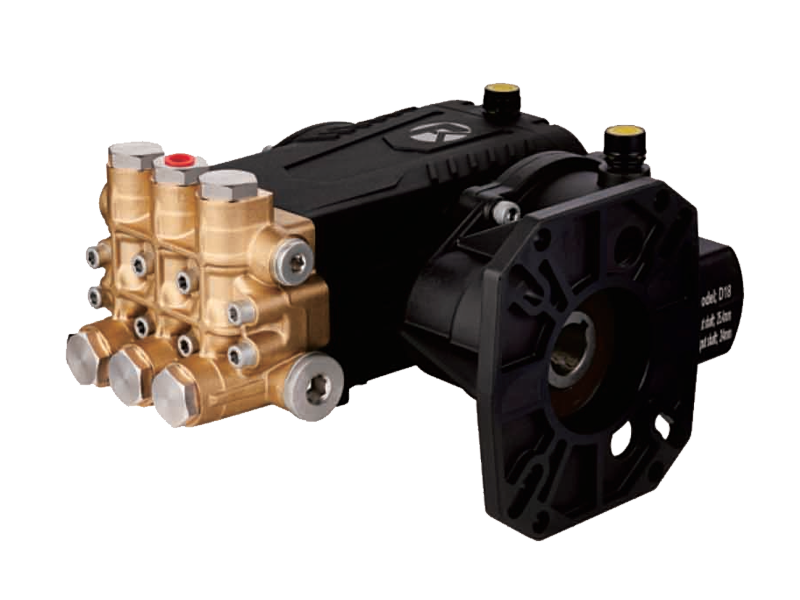
High Pressure Pumps are widely used in various industries, including chemical processing, oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing. Due to the demanding environments they operate in, corrosion resistance is a critical factor in determining their reliability and service life. Pumps exposed to aggressive fluids, saline water, or acidic conditions require materials and designs that can withstand corrosion to prevent failures, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure safety.
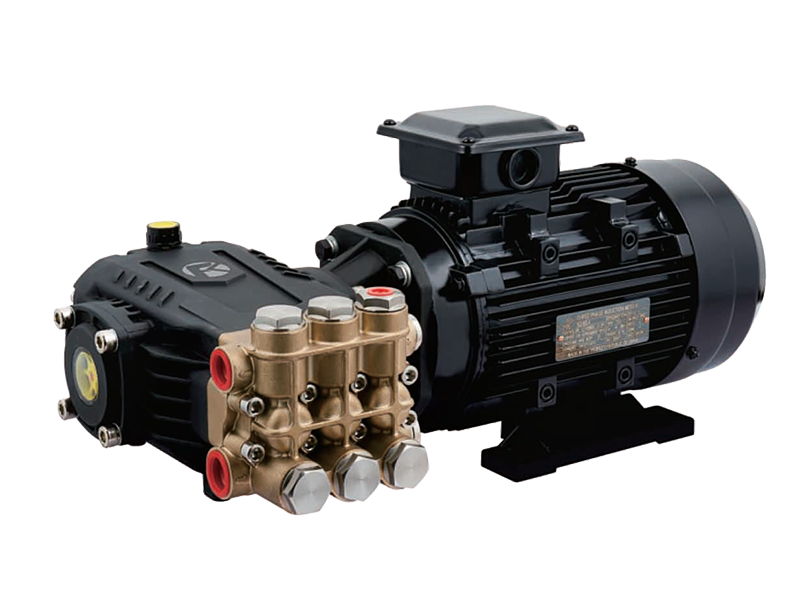
Material Selection and Its Impact on Corrosion Resistance
One of the fundamental ways to enhance a Pressure Pump’s corrosion resistance is through careful material selection. Common materials include stainless steel, duplex stainless steel, high-grade alloys such as Inconel or Hastelloy, and specialized coatings. Stainless steel, especially grades 316 and above, offers good resistance against oxidizing environments and moderate chemical exposure. Duplex stainless steels provide better strength and corrosion resistance in chloride-rich or seawater environments. In more aggressive media, high-performance alloys or protective surface treatments become necessary to extend pump longevity.
Design Features That Minimize Corrosion Risks
Beyond materials, the design of a high-pressure pump also plays a significant role in corrosion resistance. Pumps designed with smooth internal surfaces and crevices reduce areas where corrosive substances can accumulate and accelerate degradation. Seals and gaskets made from corrosion-resistant materials help prevent leaks that could exacerbate corrosion problems. Additionally, modular designs facilitate easier replacement of parts exposed to corrosive fluids, ensuring maintenance can be performed without compromising the entire system.
Corrosion Resistance in Various Operating Environments
The specific operating environment heavily influences the pump’s corrosion resistance requirements. In seawater desalination or offshore applications, exposure to saltwater demands materials that resist chloride-induced corrosion. Chemical plants handling acids, alkalis, or solvents require pumps with tailored material and seal configurations to prevent chemical attack. Even water treatment processes that involve chlorination or disinfection agents necessitate pumps that can withstand these chemicals without rapid deterioration.
Testing and Certification for Corrosion Performance
Reliable High Pressure Pumps undergo rigorous testing to verify their corrosion resistance before deployment. Standardized corrosion tests, such as salt spray, pitting resistance equivalent number (PREN) evaluation, and immersion testing in aggressive fluids, provide data on expected performance. Certifications from recognized bodies ensure that pumps meet industry standards for corrosion resistance, giving users confidence in their suitability for harsh environments.
Maintenance and Monitoring to Prolong Corrosion Resistance
Even the materials and designs require proper maintenance to sustain corrosion resistance over time. Regular inspections for signs of corrosion, timely replacement of seals, and maintaining appropriate operating conditions are essential. Some modern High Pressure Pumps incorporate sensors and remote monitoring capabilities to detect early corrosion or leaks, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Conclusion: Ensuring Long-Term Reliability Through Corrosion-Resistant High Pressure Pumps
In conclusion, a high-pressure pump’s ability to resist corrosion depends on a combination of material quality, design considerations, environmental factors, and maintenance practices. Selecting pumps made from corrosion-resistant materials tailored to the specific application environment, along with regular monitoring, ensures durability and operational safety. This approach reduces lifecycle costs and enhances the efficiency of systems relying on high pressure pumping technology.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский









