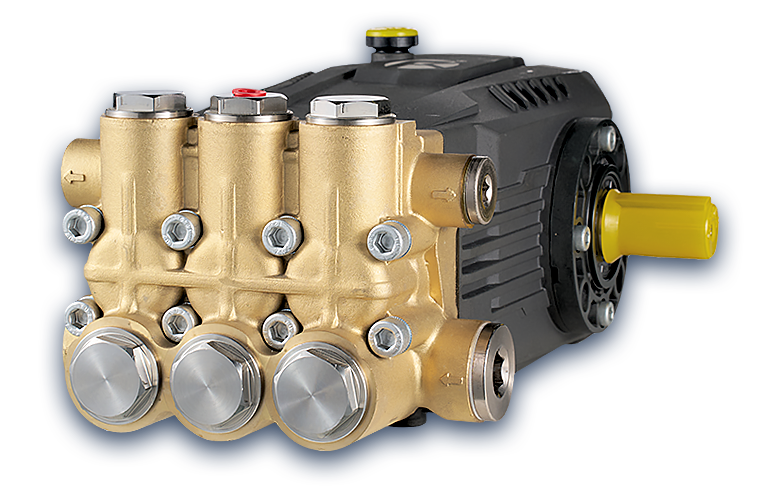
Assessing the Corrosion Resistance and Durability of Three Plunger High Pressure Pumps
Importance of Corrosion Resistance in High-Pressure Pumps
High-pressure pumps are widely used in industries where harsh conditions and aggressive fluids pose challenges to equipment durability. The Three Plunger High Pressure Pump is favored for its robust performance, but its corrosion resistance is a critical factor determining its lifespan and reliability. Corrosion can cause material degradation, leaks, and failure, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. This article explores the corrosion resistance of these pumps, the materials and design features involved, and how they withstand demanding environments.

Material Selection and Its Impact on Corrosion Resistance
A fundamental factor in the corrosion resistance of the Three Plunger High Pressure Pump is the choice of materials used in its construction. Commonly, high-grade stainless steel, duplex steel, or specialized alloys are employed for the pump’s plungers, cylinders, and valves. These materials are selected for their ability to resist oxidation, chemical attack, and mechanical wear. Additionally, coatings or surface treatments such as electropolishing or ceramic lining may be applied to enhance resistance further. Material quality directly affects how well the pump withstands corrosive fluids such as acids, seawater, or chemical solvents.
Design Features That Enhance Corrosion Protection
Beyond materials, the pump’s design contributes significantly to corrosion resistance. The Three Plunger High Pressure Pump often incorporates precision machining and tight tolerances to reduce areas where corrosive agents can accumulate. Sealing systems are engineered to prevent fluid leakage and ingress of contaminants that could accelerate corrosion. Moreover, the pump’s plunger configuration ensures balanced forces, reducing vibration and mechanical stress that might otherwise compromise protective coatings or seals.
Resistance to Different Types of Corrosive Environments
The corrosion resistance of a Three Plunger High Pressure Pump varies depending on the fluid being handled. In acidic environments, the use of acid-resistant alloys and coatings is critical to prevent rapid degradation. For pumps operating in marine or brackish water conditions, corrosion-resistant stainless steel grades and protective treatments combat chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion. In chemical processing, the ability to withstand aggressive solvents and high temperatures requires specialized materials and design adaptations.
Maintenance Practices to Prolong Corrosion Resistance
Proper maintenance is essential to preserving the corrosion resistance of these pumps. Regular inspection for signs of corrosion, timely replacement of seals and gaskets, and adherence to recommended cleaning protocols can prevent damage escalation. Additionally, flushing the pump with neutralizing or protective fluids after handling corrosive media reduces residue buildup. Following manufacturer guidelines for operating pressures and temperatures helps avoid conditions that may accelerate corrosion.
Benefits of Corrosion Resistance for Operational Efficiency and Longevity
Effective corrosion resistance enhances the operational efficiency of Three Plunger High Pressure Pumps by maintaining smooth internal surfaces and preventing leaks. This reliability reduces unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Furthermore, longer service life results in better return on investment and less environmental impact from pump replacements. In industries like oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment, corrosion-resistant pumps are indispensable for safe and continuous operations.
Innovations and Future Trends in Corrosion-Resistant Pump Technology
Ongoing research focuses on new materials such as advanced composites and nano-coatings that promise even greater corrosion protection. Smart sensors integrated into pumps can monitor corrosion levels in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing failure risks. Manufacturers are also exploring modular designs that facilitate easy replacement of corroded components without dismantling the entire pump, enhancing uptime and reducing costs.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский










