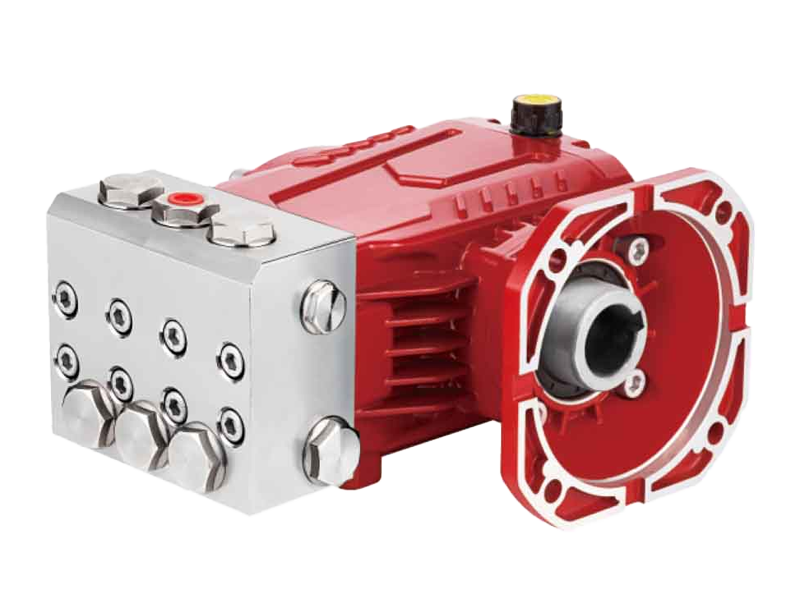
What Are the Safety Considerations When Using a Chemical Piston Pump?
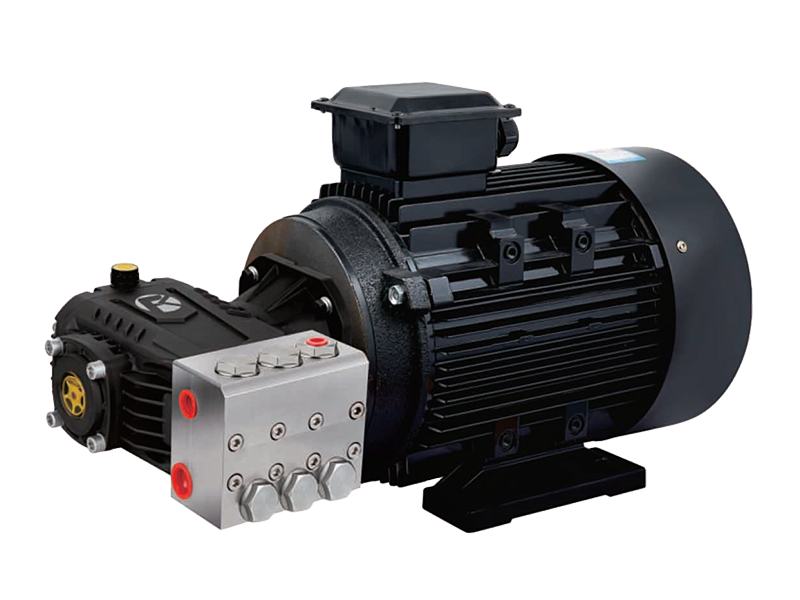
When using a chemical piston pump, safety should always be a top priority. These pumps are designed to handle and transfer various chemicals, often under high pressure, making them essential in industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and wastewater treatment. However, due to the nature of their operation and the materials they pump, there are specific safety precautions that must be taken to prevent accidents and ensure good performance.

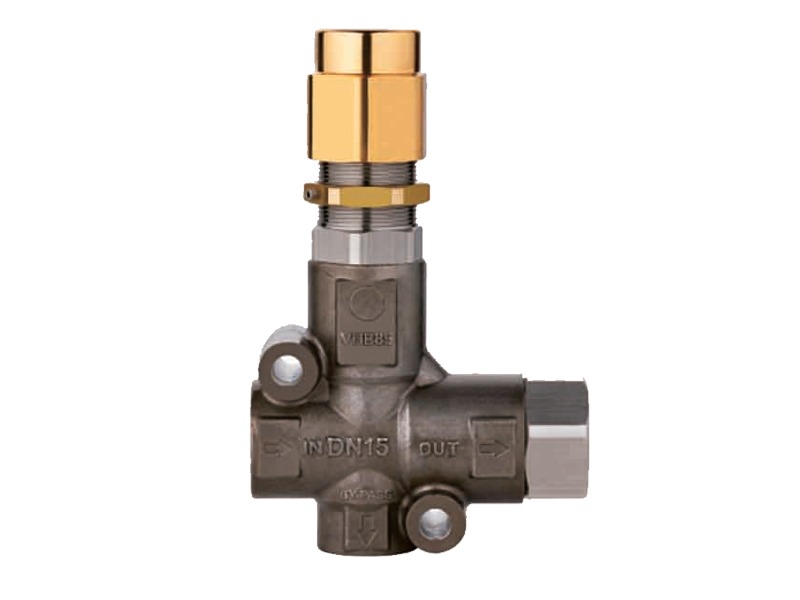
1. Proper Pump Selection and Compatibility
safety consideration when using a chemical piston pump is ensuring that the pump is compatible with the chemicals being used. Not all piston pumps are designed to handle all types of chemicals, as certain substances can cause wear, corrosion, or damage to the pump components. For example, an axial piston pump may be better suited for certain fluids, while others like highly corrosive chemicals may require a specialized chemical piston pump made from resistant materials such as stainless steel or ceramic.
Before starting any operation, always check the chemical compatibility charts provided by the pump manufacturer to confirm that the pump's materials can withstand the chemicals being transferred. Using the wrong type of pump can result in equipment failure or dangerous leaks.
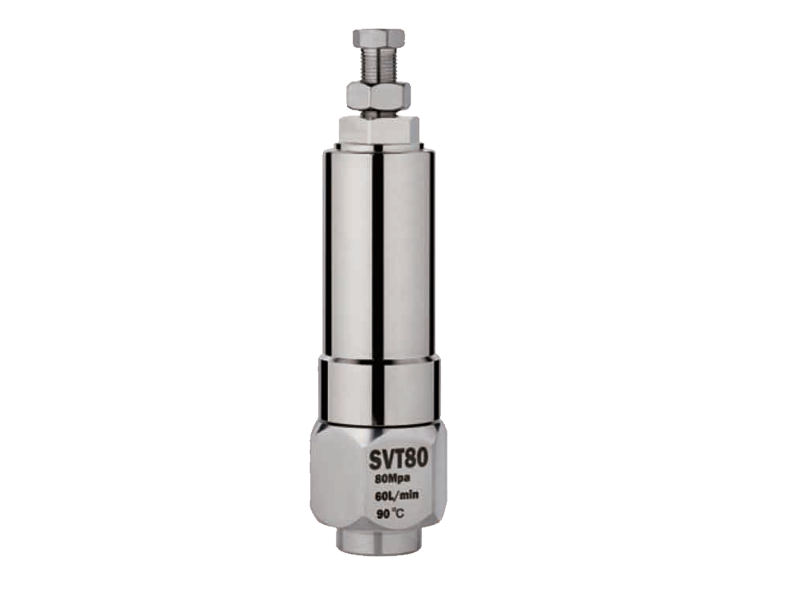
2. Pressure Control and Overload Protection
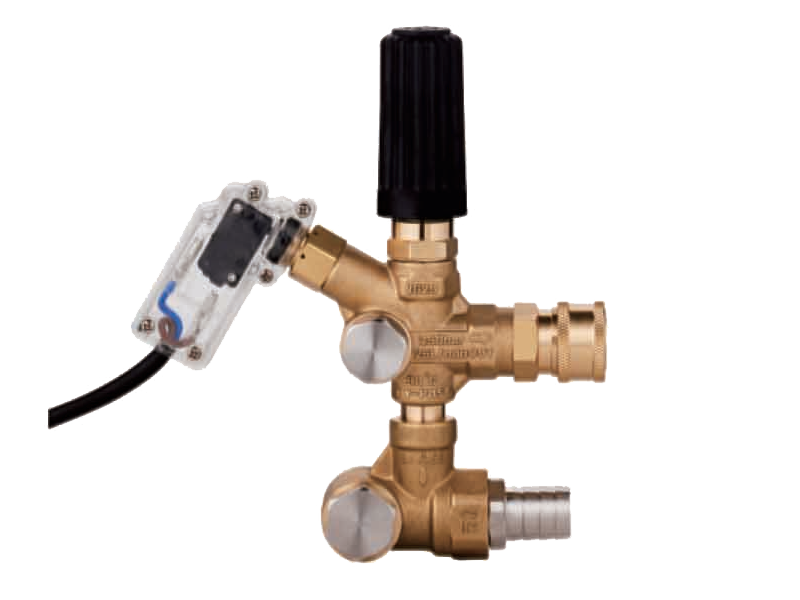
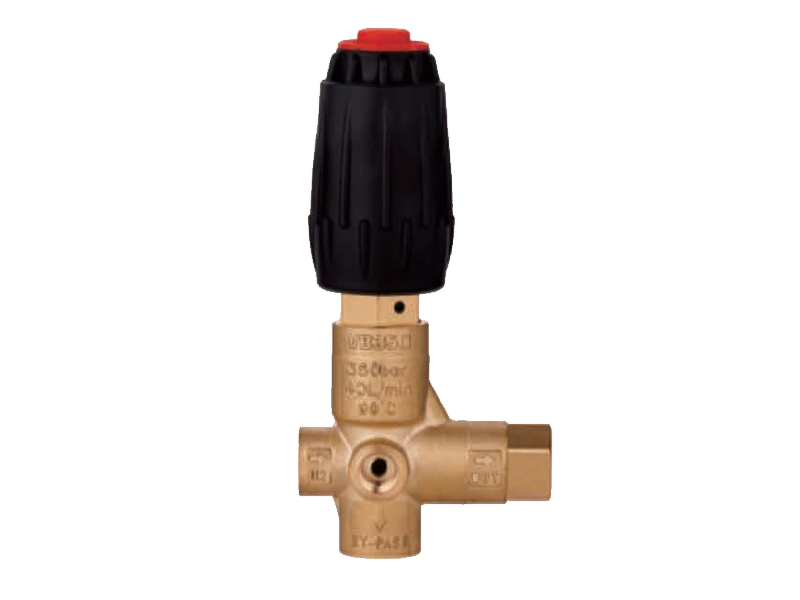
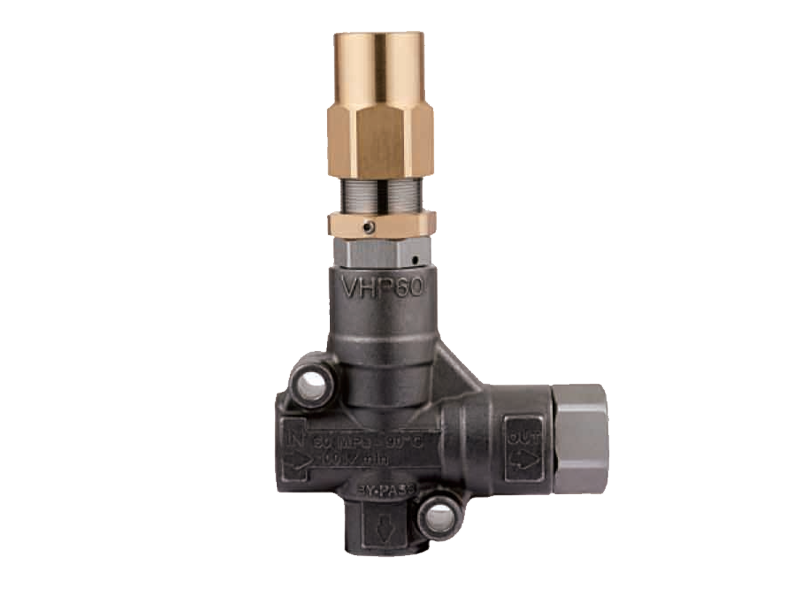
Both chemical piston pumps and axial piston pumps often operate at high pressures, which increases the risk of equipment failure or accidents if the pressure is not properly managed. It is essential to have reliable pressure control and overload protection mechanisms in place. For instance, installing pressure relief valves or regulators can help ensure that the system does not exceed its rated pressure limits.
In many cases, hydraulic driven pressure washers that utilize chemical piston pumps are designed to operate at high pressures for cleaning purposes. If the pressure exceeds safe operating levels, it can cause ruptured hoses, leaking chemicals, or even pump damage. Regularly inspect and test these safety features to ensure they are functioning correctly.
3. Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance is crucial for the safe operation of a chemical piston pump. Over time, seals, valves, and other internal components can wear out, cause leaks or pressure issues. For pumps such as axial piston pumps, the internal pistons may experience wear from continuous operation, especially if they are used in demanding conditions.
Routine inspections should include checking for signs of leaks, corrosion, or wear on critical components. Also, ensure that the lubrication system is working properly, as insufficient lubrication can cause excessive friction and overheating, which can damage the pump or create unsafe operating conditions.
Additionally, ensure that all hoses and connections are secure and free from damage, as loose or damaged hoses can cause hazardous chemical spills or pressure loss.
4. Protective Gear and Ventilation
When operating chemical piston pumps or any high-pressure equipment, it is crucial to wear appropriate protective gear. This includes gloves, goggles, and protective clothing to shield yourself from chemical exposure, as well as respiratory protection if toxic fumes are involved.
For hydraulic driven pressure washers that use chemical piston pumps, adequate ventilation is essential to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes or vapors. Work in well-ventilated areas or use fume extraction systems to ensure that workers are not exposed to hazardous substances.
5. Chemical Handling and Storage
Handling chemicals safely is another critical aspect when using chemical piston pumps. Always follow the recommended safety procedures for the chemicals being used. This includes proper storage, labeling, and disposal methods. Ensure that all chemicals are stored in secure, properly labeled containers to prevent accidental mixing or spills.
When filling the pump with chemicals, be cautious to avoid overfilling, and ensure that no chemical vapors or spills occur. In case of a spill, immediately follow the emergency response procedures to contain and neutralize the chemicals.
7.Emergency Shutdown Procedures
Every chemical piston pump setup should have a clear emergency shutdown procedure in place. In the event of a malfunction or an unsafe situation, it's important to quickly stop the operation to prevent further damage or harm. Operators should be familiar with how to shut down the pump safely and should have access to emergency shutoff switches or valves.
Additionally, maintaining a clear communication system between operators and supervisors can ensure that any issues are addressed promptly and safely.
By ensuring the pump is compatible with the chemicals being used, maintaining proper pressure control, conducting regular inspections, and following proper handling procedures, operators can minimize risks and ensure safe, efficient operation.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский










