Analyzing Energy Efficiency of Three Plunger High Pressure Pump Under Variable Loads
Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a critical consideration in industrial operations, affecting both operational costs and environmental impact. High-pressure pumps, such as the Three Plunger High Pressure Pump, are commonly used in water treatment, chemical processing, and oil extraction. These applications often involve fluctuating loads and varying flow demands. Understanding how the pump performs in terms of energy efficiency under different load conditions is essential for optimizing operation, reducing energy waste, and ensuring long-term cost-effectiveness.
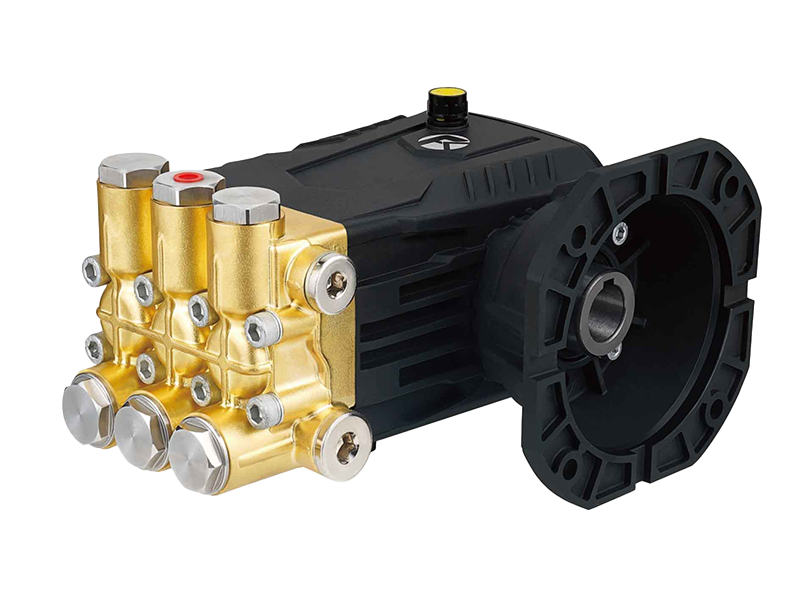

Design Features Influencing Energy Consumption
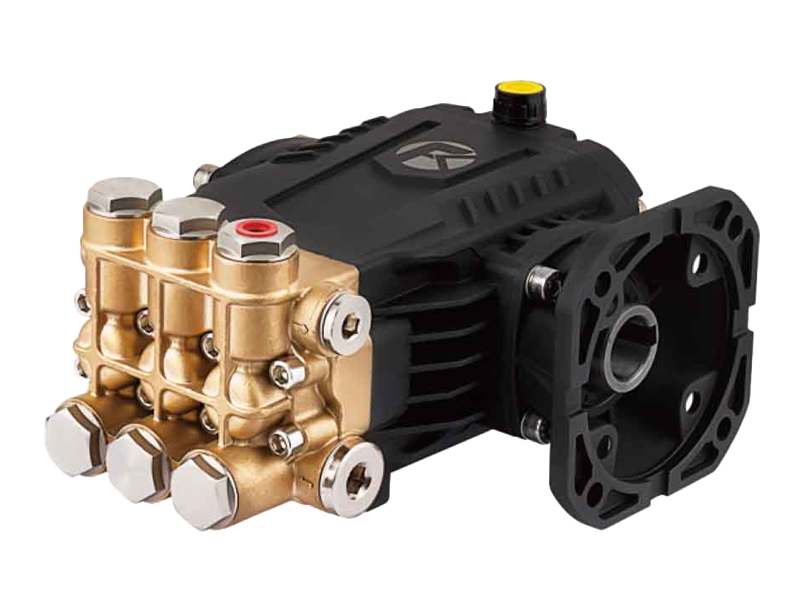
The Three Plunger High Pressure Pump is designed with multiple pistons to distribute workload evenly, which inherently improves energy efficiency. Each plunger operates in sequence, maintaining a continuous flow and reducing pressure spikes. The mechanical design, including low-friction bearings, high-precision plunger alignment, and optimized valve arrangements, reduces energy losses. These features allow the pump to maintain a relatively stable energy consumption profile, even when faced with moderate fluctuations in load.
Energy Consumption at Low Load
At low operating loads, the pump consumes less energy due to reduced hydraulic resistance and lower fluid displacement requirements. However, inefficiencies may arise if the pump operates significantly below its suitable design range. Excessive idling or partial load conditions can cause higher relative energy losses per unit of fluid delivered. Understanding the load requirements and adjusting operation to remain within an efficient range helps optimize energy performance and reduce unnecessary electricity consumption.
Performance Under Medium Load Conditions
Medium load operation generally represents the pump’s suitable efficiency range. The Three Plunger High Pressure Pump maintains consistent flow and pressure while reducing frictional and hydraulic losses. At this range, energy consumption per unit of fluid displaced is balanced, and the pump’s components operate under ideal conditions, reducing wear and tear. This efficiency makes medium load operation particularly advantageous for processes with steady demand, contributing to both energy savings and longer equipment life.
Energy Demand at High Load
High load conditions require the pump to generate pressure and flow rates, which increases energy consumption. Although the three-plunger design distributes the workload, the mechanical and hydraulic resistance rise, causing a higher power draw. Continuous operation at peak load can also generate additional heat, necessitating cooling or lubrication systems that further impact energy usage. Proper monitoring and management of peak load periods are critical to prevent excessive energy consumption while ensuring the pump meets operational requirements.
Strategies to Improve Energy Efficiency
To optimize energy performance under varying loads, operators can implement several strategies. Using variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows the pump speed to adjust according to demand, reducing unnecessary energy usage during low or moderate load periods. Regular maintenance ensures that seals, valves, and plungers operate smoothly, reducing frictional losses. Additionally, monitoring system pressure and flow in real-time helps identify inefficiencies and make adjustments promptly. Implementing these practices ensures that the Three Plunger High Pressure Pump operates efficiently across all load conditions.
Balancing Performance and Energy Use
The Three Plunger High Pressure Pump exhibits varying energy consumption depending on the load, with suitable efficiency typically achieved at medium operational loads. Low and high load conditions require careful management to prevent energy waste and ensure stable performance. By leveraging design advantages, monitoring operational parameters, and employing strategies such as VFDs and regular maintenance, operators can improve energy efficiency while maintaining reliable performance across different load scenarios. Efficient energy management not only reduces operational costs but also extends the service life of the pump.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский










